44 label the atp molecule
Bio Cp 1-ATP/ADP Molecules quiz Flashcards | Quizlet ATP Energy from food Energy released... ADP + P Label the following diagram Adenine (the two octagons things-FAR LEFT) Ribose (the single, darker, big Pentagon-THE MIDDLE ONE) Three Phosphate Groupes (The black circles with the white P in the middle-FAR RIGHT) Define Cell Energy... The ability to do cell work. Which label identifies the part of the ATP molecule that changes when ... Explanation: Adenosine triphosphate, commonly known as ATP, is the energy carrier molecule in living cells. ATP is structurally composed of Adenine molecule (a nitrogenous base), Ribose (pentose sugar) and three phosphate groups. Energy in ATP is stored in the bonds that hold the phosphate groups together.
Enzymes and ATP-ADP Flashcards - Quizlet Explain the purpose of a molecule of ATP and where most of the energy is stored in a molecule. the purpose for ATP carries/ stores energy for the cell function. the energy is stored in the Mitachondria. Draw the structure and label the parts of a molecule of ATP. describe the ATP- ADP cycle. Include what is and is not recycled.
Label the atp molecule
Label the parts of an ATP molecule? - Answers The three parts of an ATP, adenosine triphosphate, molecule are:A sugar (ribose)3 phosphates (the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate bonds)Adenine (a double ring of carbon and... ATP Diagram | Quizlet a lower-energy molecule that can be converted into ATP. Tri. three. Di. two. ATP Cycle. a cycle that converts ADP into ATP & ATP releases energy and turns into ADP. Phosphate Group (removed) a phosphate is removed to release energy. Phosphate Group (added) A phosphate group is added using a small amount of energy. atp molecule Flashcards and Study Sets | Quizlet every cell on earth used ATP to do work. ATP has energy that cells can directly use for cell processes. Active transport muscle movement chemical reactions. breaking the bond between the second and third phosphate group. Why is ATP considered the universal ene…. every cell on earth used ATP to do work.
Label the atp molecule. Model of ATP Molecule | Perkins eLearning The model described is of a molecule of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) which is the energy currency of the cell because it provides energy for the cell's activities. Understanding the structure of this molecule leads to a clear understanding of the manner in which it provides needed energy to the cell. This model was created by Adele Hauser ... Which label identifies the part of the ATP molecule that changes when ... Answer: C; respiration. Explanation: Cellular respiration is the process by which nutrients such as glucose are broken down using oxygen to generate energy in the form of ATP, that is used to drive cellular processes.; ATP consists of an adenosine molecule bonded to three phosphate groups in a row. Energy from cellular respiration is stored in the bond between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups ... Physiology, Adenosine Triphosphate - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf The body is a complex organism, and as such, it takes energy to maintain proper functioning. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the source of energy for use and storage at the cellular level. The structure of ATP is a nucleoside triphosphate, consisting of a nitrogenous base (adenine), a ribose sugar, and three serially bonded phosphate groups. ATP is commonly referred to as the "energy currency ... Describe the three parts of an ATP molecule? - Answers The parts of a molecule of ATP are:* the purine base, adenine, linked to * the sugar, ribose, linked to * a chain of three phosphate groups. ... Label the parts of an ATP molecule? Adedine, Ribose ...
Unit 7.pdf - 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Make sure... Draw and label an ATP molecule. Make sure to include the 3 parts. 2. What is the process called when a phosphate is added to the ADP molecule a. Photosynthesis b. Phosphorylation c. Permeability d. Precipitation. 3. The metabolism (breakdown) of _____ in the mitochondria provides the energy for the phosphorylation of ADP. a. ATP b. What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Adenine, Ribose, and three Phosphate groups. ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine Ribose Three Phosphate Groups Here is a picture: CR Study guide.pdf - 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule.... 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how ATP molecules release energy (including the enzyme responsible). 2. Why is ATP important? ATP is important because it supplies energy for our cells; without it we would not have the energy to grow, move, etc. Ribose P Adenine P Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - HHMI BioInteractive Description This model shows the structure of ATP, a molecule that provides energy for cellular processes, including protein phosphorylation. ATP has many important roles in the cell. A major role of ATP is to bind to and activate enzymes called kinases.
Arabidopsis guard cell chloroplasts import cytosolic ATP for starch ... 03-02-2022 · Stomatal opening requires the provision of energy in the form of ATP for proton pumping across the guard cell (GC) plasma membrane and for associated metabolic rearrangements. The source of ATP ... Green fluorescent protein - Wikipedia The green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a protein that exhibits bright green fluorescence when exposed to light in the blue to ultraviolet range. The label GFP traditionally refers to the protein first isolated from the jellyfish Aequorea victoria and is sometimes called avGFP.However, GFPs have been found in other organisms including corals, sea anemones, zoanithids, copepods … Photosynthesis: Crash Course Biology #8 - YouTube Hank explains the extremely complex series of reactions whereby plants feed themselves on sunlight, carbon dioxide and water, and also create some by product... Fluorescence Polarization Assays in Small Molecule Screening Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) has been suggested as a target for cancer therapy, with most available inhibitors acting as ATP competitors within the Plk1’s conserved ATP binding site . In order to search for monospecific inhibitors, Reindl et al . conducted a screening campaign to target Plk1 polo-box domain (PBD) PPI which mediates intracellular localization of Plk1.
Unit_7_ (2).docx - 1 Draw and label an ATP molecule. Make... 1 Draw and label an ATP molecule. Make sure to include the 3 parts. (Drawing was made on a separate piece of paper) ( Drawing was made on a separate piece of paper ) 2 What is the process called when a phosphate is added to the ADP molecule a. Photosynthesis b. Phosphorylation c. Permeability d. Precipitation
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. All living things use ATP.
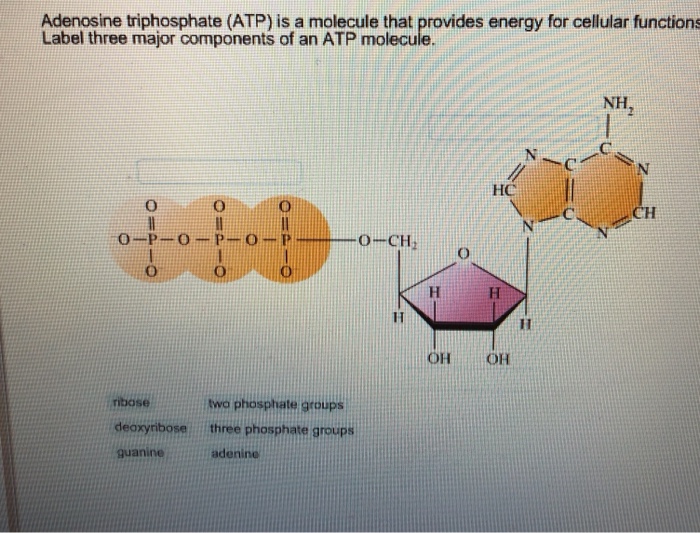
Solved Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that | Chegg.com Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that provides energy for cellular functions. Label three major components of an ATP molecule. NH, Answer Bank guanine three phosphate groups v=CH deoxyribose adenine -O-P-0 - P-0 — -0-CH ribose k H H two phosphate groups ОН ОН
ATP synthesis and storage - PMC 12-04-2012 · It has been calculated that, for the synthesis of one ATP molecule, four protons are required (three for the ATP synthase rearrangements and one for ATP, ADP, ... Wang Y, Liu B. ATP detection using a label-free DNA aptamer and a cationic tetrahedralfluorene. Analyst. 2008; 133 (11):1593–1598.
The ATP Molecule -Chemical and Physical Properties The Adenosine triphosphate ( ATP) molecule is the nucleotide known in biochemistry as the "molecular currency" of intracellular energy transfer; that is, ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids. For 3-D Structure of this image using Jsmol Click here
Structure of ATP - Learn Insta The ATP molecule is composed of three components. These phosphates are the key to the activity of ATP. ATP consists of a base, in this case adenine (red), a ribose (magenta) and a phosphate chain (blue). All living things, plants and animals, require a continual supply of energy in order to function. The energy is used for all the processes ...
Insights into the client protein release mechanism of the ATP ... 20-05-2022 · How ATP-independent chaperones release their clients without energy input remains enigmatic. ... To model the PRE spin label, an MTSL molecule was attached to the N-terminal cysteine residue.
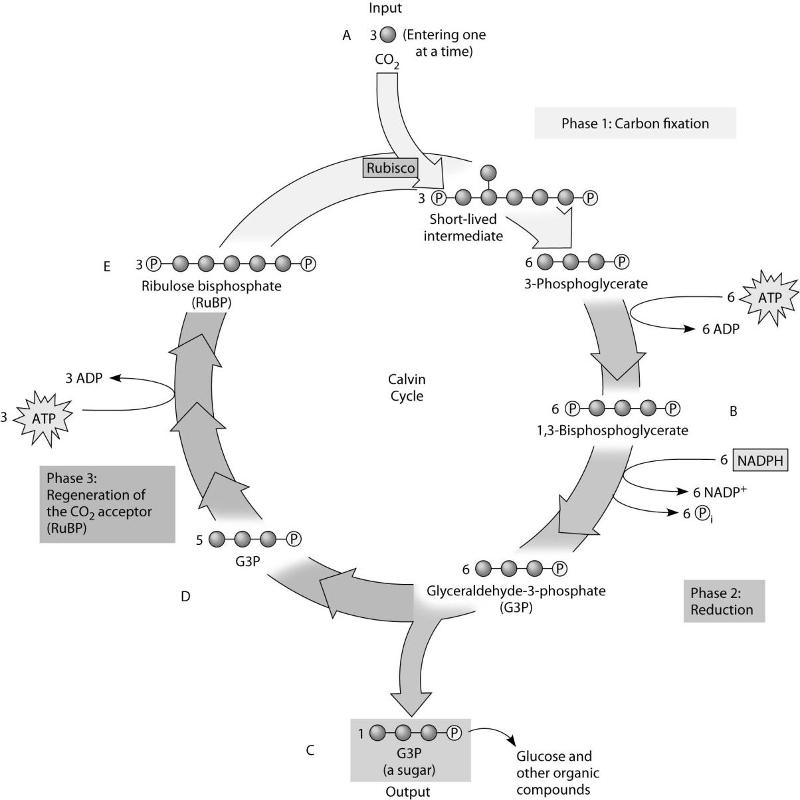
Photosynthesis Flashcards | Quizlet Label diagram 7 with three phases of the Calvin cycle. Phase 1: Fixation Phase 2: Reduction Phase 3: Regeneration ... The electron from a molecule of water goes with H+ to the ATP Synthase, to which it joins the sugar G3P. Describe how ATP is produced in the light reactions.
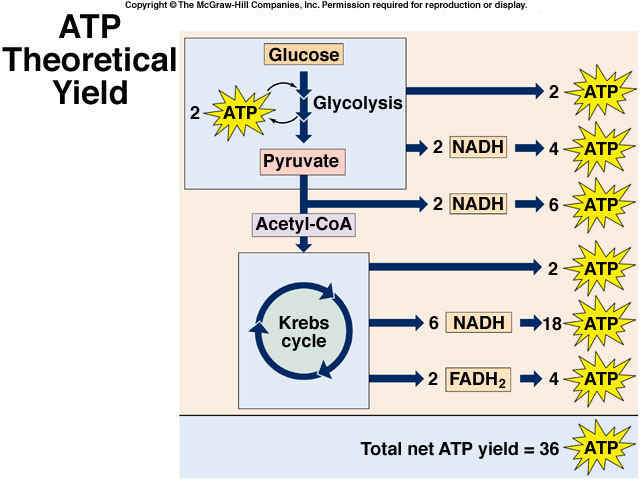
LAB 6 Fermentation & Cellular Respiration While 2 ATP per glucose molecule is clearly better than nothing, it is not nearly enough to meet the energy needs of complex multicellular organisms such as plants and animals. To get the maximum ATP yield from molecules of glucose requires cellular respiration, which and produce up to 36 ATP per glucose molecule.


Post a Comment for "44 label the atp molecule"